Size is important to your overall shooting experience when choosing a handgun. Whether you’re considering a firearm for concealed carry, home defense, or recreational shooting, understanding the different handgun sizes will help you make the best decision for your needs.
Why Handgun Size Matters
Impact on Carry Comfort and Concealability
One of the primary reasons handgun size is so important is its effect on how comfortably and discreetly you can carry it.
Smaller handguns are designed for easy concealment. Their reduced size and weight make them ideal for everyday carry. On the other hand, larger handguns can be more cumbersome to carry and may require specialized holsters or carry methods.
Recoil Management and Shooting Accuracy
The size of your handgun also plays a significant role in recoil and accuracy.
Larger handguns generally have more weight and surface area to absorb the energy released during firing, which can help mitigate recoil. This makes them easier to control, especially for rapid follow-up shots.
Conversely, smaller handguns tend to have more pronounced recoil due to their lighter weight and shorter barrels. While they offer greater portability, this can make them more challenging to shoot accurately (especially for beginners or those with less hand strength).
Suitability for Different Purposes
Handgun size is also a determining factor when considering your gun’s purpose.
Compact and subcompact pistols are often preferred for self-defense because they combine concealability with sufficient firepower. They are small enough to be easily carried and still pack enough punch to be effective in a defensive situation.
In contrast, full-size handguns are often the go-to choice for sport shooting or competitive events. Their larger frames provide better stability and accuracy and typically have higher magazine capacities that reduce reload frequency.
If you’re a woman shooter, you have other factors to consider when choosing a handgun. Check out The Best Handguns for Women for a deeper dive into these other elements.
Categories of Handgun Sizes
Here’s a breakdown of the primary handgun size categories:
Full-Size Handguns

Full-size handguns (aka standard handguns) are typically the largest category.
- They feature longer barrels, larger grips, and larger magazine capacities than their smaller counterparts.
- These handguns often measure around 7 to 9 inches in length and are designed to provide the best balance between performance and handling.
- Full-size handguns offer improved sight radius and accessory options, such as tactical lights.
- Standard calibers include 9mm, .45 ACP, .40 S&W, .357 SIG, 10mm, and .38 Super, chosen for their stopping power, recoil management, and performance.
- They can weigh over 2 pounds when fully loaded.
Some well-known examples of full-size handguns include:
- Glock 17: Renowned for reliability and widely used in law enforcement and military applications.
- SIG P226: Another favorite among law enforcement and military personnel, it is known for its accuracy and durability.
- Beretta 92FS: Trusted by the U.S. military for decades, celebrated for its reliability and ergonomic design.
Best Uses and Benefits
Full-size handguns excel in several areas:
- Home defense: Their larger size allows for a more stable grip and better control, which can be crucial in high-stress situations. The increased magazine capacity also means fewer reloads during an emergency.
- Sport shooting: Full-size handguns are ideal for competitive shooting and target practice. Their longer barrels provide better accuracy, and the larger frames help manage recoil more effectively, allowing quicker follow-up shots.
- Law enforcement and military: Full-size handguns are often the standard issue for many law enforcement agencies and military units due to their robustness and reliability.
Mid-Size Handguns

Mid-size handguns strike a balance between the large full-size models and the smaller subcompact versions. Although sometimes called “compact,” they are distinct from compact guns.
- They measure around 6.5 to 7.5 inches in overall length and are designed to offer a blend of maneuverability and firepower.
- These handguns are slightly smaller than full-size, making them easier to carry concealed while still providing good handling and accuracy.
- Mid-size handguns often boast a long sight radius to aid in accuracy, and they can typically be equipped with various accessories such as lights and laser sights.
- Popular calibers are 9mm, .40 S&W, .45 ACP, .357 SIG, and .380 ACP, offering versatility, stopping power, and manageable recoil.
- The handguns typically weigh between 1 to 2 pounds when loaded.
Popular examples of mid-size handguns include:
- Glock 19: Known for its versatility and reliability, the Glock 19 is a favorite among civilian and law enforcement users.
- SIG P229: Recognized for its precision and performance, it’s widely used by law enforcement agencies.
- Smith & Wesson M&P 2.0: It offers a great balance of size and capacity.
Best Uses and Benefits
Mid-size handguns present several advantages, catering to multiple uses:
- Concealed carry: Their reduced size compared to full-size handguns makes them easier to conceal under clothing while maintaining a comfortable grip and sufficient barrel length for accurate shooting.
- Home defense: These handguns compromise size and capacity, making them an excellent choice for home defense. They provide better control and more rounds per magazine than subcompacts while still manageable in high-stress situations.
- All-around use: Mid-size handguns are versatile and suitable for various activities, from shooting at the range to more serious defensive applications. This makes them ideal for those seeking a single handgun that can fulfill multiple roles.
Compact Handguns
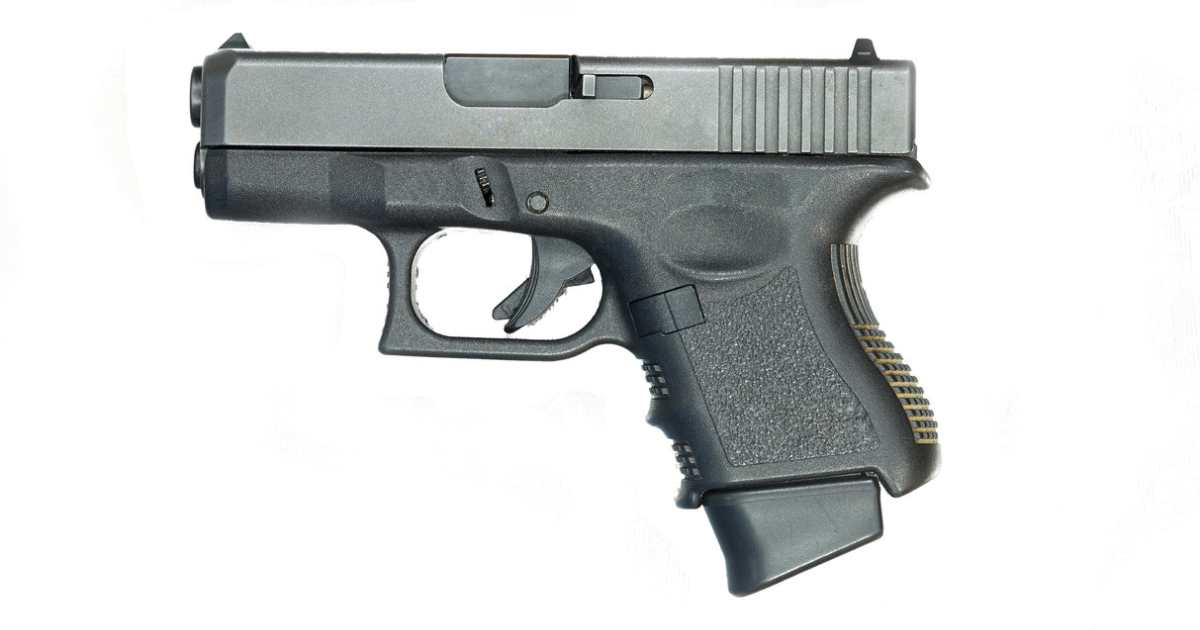

Compact handguns are designed to balance concealability and performance, making them popular for everyday carry and personal defense.
- Compact handguns measure around 6 to 7 inches in length.
- They feature shorter barrels and grips than full-size models, making them easier to conceal while maintaining a decent magazine capacity and shootability.
- Compact handguns often come with accessory rails for lights and lasers, and their shorter sight radius is offset by their enhanced portability.
- Commonly chambered in 9mm, .40 S&W, .45 ACP, .380 ACP, and .357 SIG for effective performance and carry.
- They range from less than a pound to 1.5 pounds with a loaded magazine.
Popular examples of compact handguns include:
- Glock 26: Often referred to as the “baby Glock,” popular for its compact size and high capacity.
- SIG Sauer P365: Renowned for packing a large magazine capacity into a small frame.
- Springfield XD-S: Celebrated for its slim design and powerful performance.
Best Uses and Benefits
Compact handguns excel in several areas:
- Concealed carry: They’re designed to be easily concealable under clothing and more comfortable to carry for extended periods.
- Personal defense: Compact handguns offer sufficient firepower and magazine capacity for personal defense situations while providing good control and manageable recoil.
Subcompact Handguns
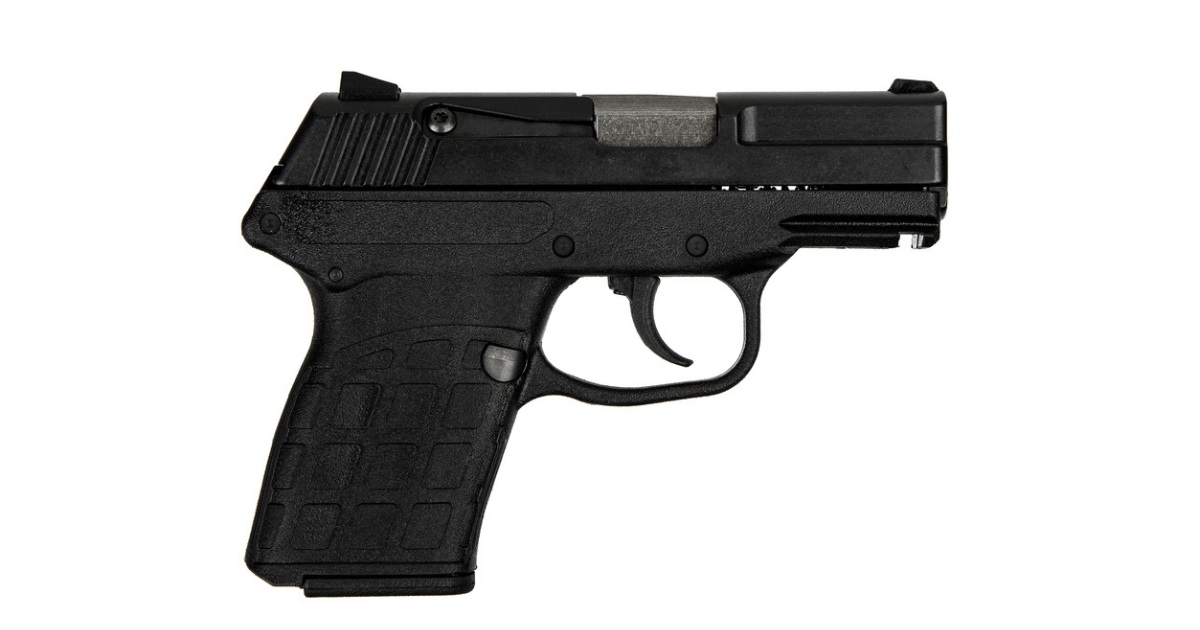

Subcompact handguns are designed to prioritize maximum concealability without sacrificing performance.
- Subcompact handguns measure around 5.5 to 6.5 inches in overall length.
- They feature shorter barrels and grips, making them easier to conceal under clothing.
- While their magazine capacity and barrel length are reduced compared to larger handguns, they still offer effective performance for close-quarters defense.
- Typically chambered in 9mm, .380 ACP, .40 S&W, .45 ACP, and .357 SIG, prioritizing concealability and recoil.
- These weigh around a pound or less when fully loaded.
Popular examples of subcompact handguns include:
- Glock 43: Known for its ultra-concealable design and reliable performance.
- SIG Sauer P938: Combines the 1911-style trigger with subcompact size, offering accuracy and control.
- Smith & Wesson Bodyguard .380: Known for its compact size and integrated laser.
Best Uses and Benefits
Subcompact handguns present several advantages for specific needs:
- Deep concealment: Subcompact handguns are designed to be easily concealed in various carry positions, and their reduced size and weight make them comfortable to carry for extended periods.
- Backup weapon: They’re often used as backup weapons for those who carry a larger primary firearm.
- Personal defense: While smaller, subcompact handguns still offer sufficient firepower and accuracy for personal defense situations.
Micro-Compact Handguns
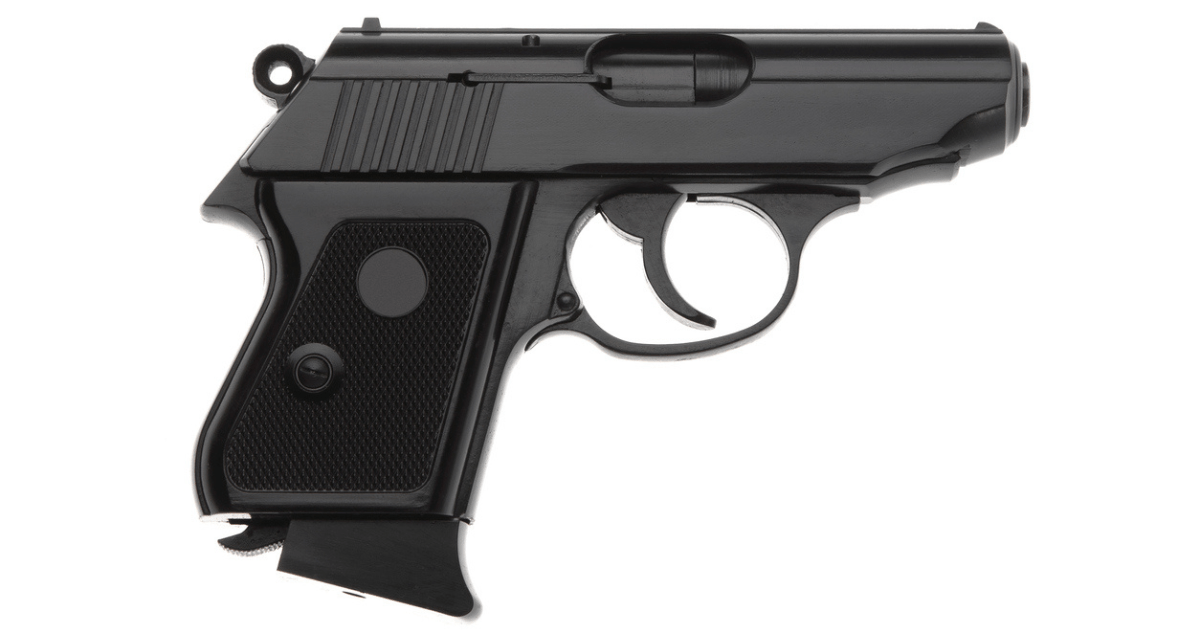

Micro handguns (aka, pocket-size handguns) are the smallest category, designed for ultimate concealability.
- These handguns measure less than 6 inches in total length and are lightweight, making them easy to carry in a pocket or small holster.
- Their compact dimensions and minimalistic design focus on portability over performance, but they still offer sufficient firepower for close-range defense.
- Due to their small size, they often have limited magazine capacity, increased recoil, and can be challenging to shoot accurately at longer distances.
- They’re usually chambered in .380 ACP, 9mm, .22 LR, and .32 ACP performance in small frames.
- They weigh less than a pound with a full magazine.
Well-known examples include:
- Ruger LCP: Known for its ultra-compact size and lightweight, the Ruger LCP is a popular choice.
- Kel-Tec P32: Known for its small size and lightweight.
- Seecamp LWS .32: Renowned for its high-quality craftsmanship and compact design.
- Beretta Tomcat .32: Known for its tip-up barrel design and ease of use.
Best Uses and Benefits
Micro-compact handguns come with several specific advantages, particularly suitable for users who prioritize discretion and convenience:
- Deep concealment: Their primary benefit is their ability to be deeply concealed. They can be carried in various ways, such as in a pocket, ankle holster, or even inside a small bag.
- Backup weapon: Law enforcement and personal security professionals often use these handguns as secondary or backup weapons. Their small size allows them to be easily carried alongside a primary firearm.
- Emergency self-defense: For those seeking a last-resort option for self-defense, pocket-size handguns are a practical solution.
Choosing the Right Handgun Size

Selecting the appropriate handgun size to carry involves considering several personal factors and understanding the pros and cons of each size. Here’s a guide to help you navigate this decision.
Factors to Consider
Body Type
- Smaller frames: Compact, subcompact, or micro handguns are more comfortable and concealable.
- Larger frames: Mid-size or full-size handguns can be carried comfortably without printing (showing the outline of the gun through clothing).
Carry Position
- Inside-the-Waistband (IWB): Suitable for all sizes, but larger handguns may require more adjustment for comfort.
- Outside-the-Waistband (OWB): More comfortable for larger handguns but harder to conceal.
- Appendix Carry (AIWB): It works well with compact and subcompact handguns, but comfort varies by body type.
- Pocket Carry: Best suited for micro-compact handguns due to their small dimensions.
Clothing Style
- Casual/loose-fitting clothing: Easier to conceal larger handguns due to the extra fabric.
- Formal/tighter clothing: Compact, subcompact, or micro handguns are preferable for maintaining discretion.
Pros and Cons of Different Sizes for Concealed Carry
Full-Size Handgun
- Pros: Higher magazine capacity, better control, and accuracy.
- Cons: Harder to conceal, heavier, and may require more substantial adjustments for comfortable carry.
Mid-Size Handgun
- Pros: Good balance between concealability and performance, suitable for various carrying methods.
- Cons: May still be challenging to conceal in tighter clothing.
Compact Handgun
- Pros: Easier to conceal, maintains good control and accuracy while being more comfortable to carry.
- Cons: Slightly reduced magazine capacity, can still be bulky for tight or minimal clothing.
Subcompact Handguns
- Pros: Highly concealable, lightweight, and compact, making them comfortable for extended periods.
- Cons: Lower magazine capacity and increased recoil, reduced accuracy and control due to smaller size and grip.
Micro Handguns
- Pros: Ultimate concealability, lightweight, and easy to carry in a variety of positions.
- Cons: Limited magazine capacity, increased recoil, and reduced accuracy.
For more help with concealed carry or EDC, check out Urban EDC Essentials and How I Juggle My EDC Items.
Tips for Testing and Selecting the Right Size
Try before you buy: Visit a range that offers rentals to test different handgun sizes and models. Pay attention to how each feels in your hand, the recoil, and how easily you can control and conceal it.
Consider your daily routine: Consider how you dress and move. Do you like your shirt tucked in? Do you wear a lot of athletic clothing? Choose a size that fits your lifestyle without causing discomfort or drawing attention.
Practice regularly: Regardless of your chosen size, regular practice is essential. It will help you draw and handle your handgun safely and effectively.
Use a quality holster: The right holster can significantly enhance the comfort and concealability of your handgun. Look for holsters designed specifically for your chosen carry position and handgun model.
For instance, our Alias System offers versatility, allowing you to carry your handgun IWB or OWB based on your needs. The design makes it incredibly easy to transfer your holster from one outfit to another, enabling you to quickly switch from a bike ride to dinner without the hassle of extensive setup.
Check out these resources for more information about the Alias System:
- Getting Started with the Alias System
- The Advantages of Using a Beltless Holster
- Balancing Quick Access and Gun Safety with the Alias System
Choosing the Right Handgun Size
Ultimately, the best handgun for you is one that you can carry comfortably, handle safely, and shoot accurately.